New Jersey Labor Laws Guide
Ultimate New Jersey labor law guide: minimum wage, overtime, break, leave, hiring, termination, and miscellaneous labor laws.
| New Jersey Labor Laws FAQ | |
| New Jersey minimum wage | $13 |
| New Jersey overtime | 1.5 times the regular wage for any time worked over 40 hours/week ($19.5 for minimum wage workers) |
| New Jersey breaks | Breaks not required by law |
Table of contents
New Jersey wage laws
With regard to wage regulations in New Jersey — state laws apply (aside from certain exempt cases in youth employment).
The following are the regulations concerning the state minimum, tipped hourly wage, and the subminimum wage in New Jersey.
| NEW JERSEY MINIMUM WAGE | ||
| Regular minimum wage | Tipped minimum wage | Subminimum wage |
| $13.00 | $5.13 | $4.25* * Exempt occupations receive the state minimum wage of $13.00. Read the section below to see the list. |
New Jersey minimum wage
As of January 1, 2022, the minimum wage in New Jersey for most workers is $13 per hour.
The state minimum wage keeps increasing each year, and it is expected to reach $15 per hour by 2024./p>
Exceptions to the minimum wage in New Jersey
Even though the New Jersey minimum wage is $13 per hour, certain employees and occupations are exempt from the state minimum.
Look at the table to see the exempt cases:
| MINIMUM WAGE EXCEPTIONS | |||
| Seasonal and small businesses with less than 6 employees | Agricultural workerse | Farm workers | Long-term care facility direct care staff members |
| $11.90 | $11.05 | $8.85 | $16 |
In addition to the exempt cases above, here are other occupations and workers that don’t qualify for the state minimum wage:
- Automobile salespersons
- Outside salespersons
- Minors under the age of 18 (See the section ‘NJ subminimum wage’ for the list of occupations where $13 applies)
- Tipped employees
- Employees at summer camps, conferences, and retreats operated by a nonprofit or religious association or corporation (only during June, July, August, and September)
Tipped minimum wage in New Jersey
A tipped employee in New Jersey receives a minimum wage of $5.13 per hour.
Under New Jersey law, a tipped employee is “any worker (full-time, part-time, or temporary) engaged in an occupation in which they customarily and regularly receive more than $30 per month in tips”.
Moreover, an employee who occasionally receives more than $30 per month — in case business was slow or the employee was on vacation — is still considered a tipped employee.
However, a tipped employee's total hourly wage plus tips must equal at least the state minimum wage of $13.00 per hour. In case it doesn’t — the employer must make up the difference.
Track work hours and calculate hourly pay with ClockifyNew Jersey subminimum wage
The New Jersey minimum wage is not applicable to minors under the age of 18, except for the following occupations and industries where the state minimum of $13.00 per hour applies:
- Mercantile occupations — Any worker selling any type of merchandise, wares, goods, or similar
- First processing of farm product occupations — Any worker engaged in the first processing, or canning, or packing, of perishable or seasonal fresh fruits or vegetables
- Hotel and motel occupations
- Food service occupations
- Minors with physical or mental disabilities
- Beauty culture occupations
- Laundry, cleaning, and dyeing occupations
- Light manufacturing and apparel occupations
Other minors employed in occupations and businesses other than the ones said are entitled to the federal youth minimum wage of $4.25 for the first 90 consecutive calendar days of employment.
Finally, full-time students are entitled to not less than 85% of the state minimum wage while the New Jersey training wage can’t be less than 90% of the minimum wage for the first 120 hours of work.
New Jersey payment law
Regarding the timing of wage payments, most employers in New Jersey are required to pay their employees at least twice a month.
Yet, some executive, supervisory and similar employees may receive their payments once a month.
Track employee payroll with ClockifyNew Jersey overtime laws
Most workers in New Jersey who work more than 40 hours in a workweek are entitled to overtime pay at a rate of one and one half (1.5) times their regular hourly wage.
However, working on a holiday, Saturday, or Sunday is not considered overtime in New Jersey.
Also, employers may require employees to work overtime provided that they don’t violate employee rights regarding wages and other employee benefits.
Special overtime regulations apply to healthcare workers.
Health Care Workers FAQsOvertime exceptions and exemptions in New Jersey
Under New Jersey law, certain salaried employees are exempt from overtime — they include:
- Bona fide executives
- Administrative employees whose earnings come at least 50% from commissions and total compensation of not less than $400 per week
- Professional employees
- Outside sales employees
- Individuals employed by a common carrier of passengers by motor bus
- Hotel workers
- Farmworkers
- Limousine drivers employed by the business that operates limousines
- Livestock workers
- Employees at summer camps, conferences, and retreats operated by a nonprofit or religious association or corporation (only during June, July, August, and September)
Fluctuating Workweek Method (FWW) in New Jersey
Luckily, some nonexempt salaried employees in New Jersey are entitled to an overtime premium of one-half (0.5) times the regular hourly wage thanks to the Fluctuating Workweek Method (FWW).
Who is eligible for FWW?
Employees who earn a fixed salary and whose workweek is “fluctuating”.
“Fluctuating” means they sometimes work 40 hours a week, sometimes more, or less.
Such workers receive the same fixed salary but are eligible for overtime pay under FWW.
Take a look at the following example:
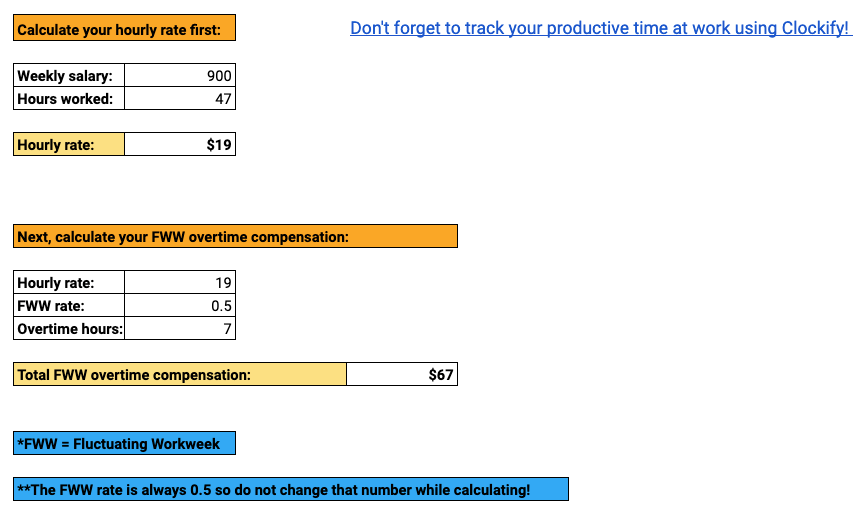
Let’s say an employee’s weekly income is $1,050, and in the preceding week, the employee worked 44 hours.
To be able to calculate overtime hours, you need to calculate the hourly rate first.
Simply divide the weekly salary by the number of hours worked for that week.
$1,050 / 44 = $24 per hour
Next, multiply the hourly rate by 0.5 for every overtime hour during the week.
$24 per hour x 0.5 = $12 for each overtime hour worked
Total overtime compensation goes as follows:
$12 x 4 overtime hours = $48
New Jersey break laws
Under federal and state law, employers in New Jersey are not obligated to provide meal or rest breaks to their employees.
Exceptions to break laws in New Jersey
Even though no federal or state laws require employers to provide rest or meal breaks, most employers do provide such breaks to maintain productivity in the workplace.
Under federal law, employers must pay employees for breaks lasting from 5 to 20 minutes while breaks longer than 30 minutes are not compensable.
Yet, if a worker is obliged to work during a meal break — for example, a factory worker who is required to remain at his machine while having lunch — such a break is paid.
Track your employee productivity with ClockifyNew Jersey breastfeeding laws
Regarding breastfeeding at the workplace, state and federal laws overlap. In such cases, regulations with better benefits for breastfeeding mothers will prevail.
That being said, breastfeeding mothers are entitled to reasonable unpaid break time for breastfeeding or expressing milk at work without time limits (unlike the federal law which limits the time to up to 1 year after the child’s birth).
Even though the federal law proposes that eligible employees are nonexempt employees — New Jersey law applies to all employees.
Moreover, both laws require an employer to provide “a suitable room other than a bathroom” for a mother to breastfeed or express milk at work.
Finally, if any of the provisions above have been violated — a complaint may be filed within 2 years of the date of the alleged violation.
Visit Wage and Hour Division for more informationNew Jersey leave requirements
The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) doesn’t require employers to pay for any time not worked.
Still, in practice, many employers do provide time off to their workers — both paid and unpaid.
Furthermore, provisions regarding public and private employees differ substantially.
In the state of New Jersey, there are two types of leave days:
- Required leave
- Non-required leave
New Jersey required leave
The following are required leaves of absence that an employer must provide to their employees in New Jersey.
They include:
- Sick leave
- Family leave
- Family and Medical Leave
- Holiday leave (public employers)
- Vacation leave (public employers)
- Jury duty leave
- Military leave
- Voting leave (public employers)
- Leave for victims of domestic violence and sexual assault
- Volunteering leave
Sick leave
Full-time, part-time, and temporary employees in New Jersey may accrue paid sick leave — for every 30 hours of work employees get 1 hour of sick leave.
They may accrue up to 40 hours of sick leave annually at the same rate of pay the employee normally earns.
Yet, employees may begin using their accrued sick leave on the 120th calendar day after the beginning of their employment.
Employees who are NOT eligible for earned sick leave include the following:
- Employees in the construction industry employed under a union contract
- Per diem health care employees
- Public employees who are provided with sick leave at full pay under any other NJ law
- Independent contractors
Family leave
The New Jersey Family Leave Act allows eligible employees to take up to 12 weeks of leave during a 24-month period. Only employers with 30 and more employees may provide such leave.
What are qualifying events for Family leave?
Eligible employees may take this leave if they have worked for the employer for at least 1 year (1,000 hours in the last year).
Also, they may take this leave in the following cases:
- Caring or bonding with a child within 1 year after the child’s birth
- Adopting or taking in a foster child
- Taking care of a family member with a serious health condition
The New Jersey Family leave doesn’t provide time off for the employee’s own health condition.
In such cases, the federal Family and Medical Leave Act comes into force.
Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA)
Under the federal Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA), eligible employees are entitled to take an unpaid leave of up to 12 weeks during any 12-month period.
What are FMLA eligible events?
Such leave of absence is taken for any of the following reasons:
- Birth and care of a newborn child
- Adopting or taking in a foster child
- Taking care of a family member (either a spouse, child, or parent) with a serious health condition
- Being unable to work due to a serious health condition
Who is covered by the FMLA?
- Employees who work in a company with more than 50 employees
- Employees who have worked for their employer for at least 12 months (1,250 hours in the last 12 months)
Holiday leave (public employers)
All state offices must remain closed on the following legal holidays in New Jersey:
- New Year’s Day (January 1)
- Martin Luther King, Jr. Day (the third Monday in January)
- Good Friday (Friday before Easter)
- Memorial Day (the last Monday in May)
- Juneteenth Day (the third Friday in June)
- Independence Day (July 4)
- Labor Day (the first Monday in September)
- Columbus Day (the second Monday in October)
- Veterans Day (November 11)
- Thanksgiving Day (the fourth Thursday in November)
- Christmas Day (December 25)
- Any general election day in New Jersey*
- Every Saturday after noon
If a legal holiday falls on a Sunday, the following Monday shall be observed as the holiday.
Also, if a legal holiday falls on a Saturday, the preceding Friday shall be observed as the holiday.
All public employees are entitled to paid days off on the foregoing legal holidays except for Lincoln’s Birthday when all offices must remain open for business.
* State employees get 2 hours of paid time off to vote — not the whole day.
Vacation leave (public employers)
Full-time state employees can accrue up to:
- 12 working days of vacation leave after 1 and up to 5 years of continuous service
- 15 working days of vacation leave after 5 and up to 12 years of continuous service
- 20 working days of vacation leave after 12 and up to 20 years of continuous service
- 25 working days over 20 years of continuous service
Jury duty leave
Jury duty is a civic responsibility of each US citizen to serve as a juror on a criminal or civil trial. In New Jersey, any employee — whether state or private — must be excused from employment to perform jury service. However, only state employees receive compensation for jury service.
Military leave
All employees in New Jersey must receive a leave of absence to perform military duty.
Following the Uniformed Services Employment and Reemployment Rights Act (USERRA), no employer can penalize, discharge, or discriminate against an employee who performs required military duty.
Furthermore, all employees have the right to regain their former jobs, wages, and other benefits following a period of service of up to 5 years.
Voting leave (public employers)
State employees in New Jersey are eligible for up to 2 hours of paid time off to vote.
Leave for victims of domestic violence and sexual assault
Under the New Jersey Security and Financial Empowerment Act (“NJ SAFE Act”), certain employees who have been victims of domestic violence or sexual assault are entitled to an unpaid leave of up to 20 days in a 12-month period.
To qualify for such leave, an employee must have at least 1,000 hours in the last 12-month period and must be employed by an employer with 25 or more employees.
Moreover, such leave may be taken by an employee whose spouse, child, or partner has been a victim of domestic violence or sexual assault.
Volunteering leave
State employees who are certified disaster service volunteers of the American Red Cross have the right to a leave of absence with pay of up to 10 workdays and additional 10 workdays of unpaid leave annually. Eligible employees must receive wages at the regular rate of pay for absent hours from work.
New Jersey non-required leave
Under federal or state law, New Jersey employers are not required to assign leave benefits to their employees. Yet, many employers do provide such benefits to their employees voluntarily. When provided, employers must act in accordance with the rights, responsibilities, and duties stated in the contract.
Non-required leaves of absence in New Jersey include:
- Holiday leave (private employers)
- Vacation leave (private employers)
- Bereavement leave
- Voting leave (private employers)
Holiday leave (private employers)
Private employees in New Jersey don’t get days off during legal holidays.
What’s more, an employer is under no obligation to pay premium wages to their employees when working on a holiday.
Vacation leave (private employers)
No law obliges private employers in New Jersey to provide employees with vacation benefits — either paid or unpaid.
Bereavement leave
This type of leave is given in case of death or to attend a funeral of the employee’s close family member, relative, or friend.
However, New Jersey employers are not required to provide bereavement leave to their employees.
Voting leave (private employers)
There is no state or federal law that obliges private employers to grant their employees time off to vote — either paid or unpaid.
Child labor laws in New Jersey
Child labor regulations in New Jersey encourage minors under the age of 18 to work — but also have strict provisions that employers must comply with.
No minor under the age of 18 is allowed to work without obtaining the employment certificate issued by the New Jersey Department of Education or the New Jersey Department of Labor and Workforce Development, known as a “A300 Combined Certification Form”.
A300 Combined Certification FormChild labor regulations include:
- Time restrictions for minors
- Breaks for minors
- Prohibited occupations
- Posting requirements
- Recordkeeping requirements
Work time restrictions for New Jersey minors
Child labor provisions in New Jersey limit the number of working hours a minor is allowed to work.
Time restrictions for minors aged 16 and 17*:
- May work no more than 40 per week
- May work no more than 8 hours per day
- May work up to 6 consecutive days in a week
- May work between 6 a.m. and 11 p.m.
- May not work before 6 a.m. or after midnight on Fridays and Saturdays or days not followed by a school day
* These time regulations for minors aged 16 and 17 apply to both school and non-school days — except when minors are allowed to work until 3 a.m. in restaurants and seasonal amusements. But minors then must have written permission from a parent if they wish to work on non-school days.
Time restrictions for minors aged 14 and 15 (when school is IN session)
- May work no more than 18 hours per week
- May work no more than 3 hours per day
- May work up to 8 hours per day on Saturday or Sunday
- May work up to 6 consecutive days in a week
- May work between 7 a.m. and 7 p.m.
Time restrictions for minors aged 14 and 15 (when school is NOT in session)
- May work no more than 40 hours per week
- May work no more than 8 hours per day
- May work up to 6 consecutive days in a week
- May work between 7 a.m. and 7 p.m.
- May work until 9 p.m. from the last day of school to Labor Day with a parents’ approval
Breaks for New Jersey minors
All employees under 18 years of age must be given a 30-minute break after 5 consecutive hours of work a day.
Prohibited occupations for New Jersey minors
No minor under 18 years of age is allowed to work in any occupation, establishment, or with machines that can present any physical, moral, or emotional hazard.
Prohibited occupations for minors under the age of 18 in New Jersey:
- Working with power-driven woodworking machinery
- Operating grinding, abrasive, polishing, or buffing machines
- Operating punch presses and stamping machines with over ¼ inch clearance
- Working near highly inflammable substances, pesticides, explosives, benzol, radioactive and carcinogenic substances, corrosive materials, noxious dust, gasses, vapors, fumes, acids, dyes, paints, colors, white, or red lead
- Working near pools and billiard rooms
Posting requirements
Every employer who employs minors under 18 years of age must display in a conspicuous place the following information:
- A list of the prohibited occupations
- A schedule of working hours
- The name of each minor and the maximum number of hours they are allowed to work each day and week
- Workday start and end times
- Break start and end times
However, said posting requirements don’t apply to the employment of minors in agricultural or domestic services, together with newspaper boys (as stated by State of New Jersey Child Labor Laws and Regulations).
Recordkeeping requirements
Employers who employ minors under 18 years of age must keep a record stating:
- Name, date of birth, and address of each employed minor
- The number of hours worked each day
- Workday start and end times
- Break start and end times
- The amount of wages paid
Employers must keep such a record on file for at least 1 year after the entry of the record.
Again, these requirements don’t apply to minors employed in agricultural or domestic services or those employed as newspaper boys under State of New Jersey Child Labor Laws and Regulations.
New Jersey hiring laws
The New Jersey Law Against Discrimination (NJLAD) is an anti-discrimination law that protects all employees from refusing to hire, pay someone less money, or promote someone based on their:
- Race
- Creed
- National origin
- Color
- Gender
- Age
- Sexual orientation
- Disability
- Marital status
- Genetic information
- Atypical hereditary cellular or blood trait
- Liability for military service
- Refusal to submit to a genetic test
However, the employer may refuse to hire a job applicant who has previously received a recruiting notice or order to report for active duty in the armed forces. Furthermore, the law allows employers to refuse to hire an individual based on sex where sex is a bona fide occupational qualification.
New Jersey termination laws
New Jersey is one of the many US states that adopted the at-will employment law.
This law allows employers to terminate an employee at any time, for any reason, or no reason at all — provided that it’s not based on illegal reasons such as discrimination, retaliation, etc.
At the same time, an employee may resign from a job without providing a reason at any time without any losses, penalties, and similar.
New Jersey final paycheck
When it comes to receiving the final paycheck due to termination of employment — whether voluntary or involuntary — the employer must pay all wages due on the regular payday.
In the event of a labor dispute, the due date may be extended for additional 10 days.
Health benefits continuation in New Jersey
Under the federal Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act (COBRA), eligible employees and their dependents get to extend their health coverage after employment termination.
Such health coverage is only temporary, and the length depends on the nature of the qualifying events under COBRA.
For instance, in case of job termination, eligible employees are entitled to another 18 months of COBRA coverage.
Furthermore, in case of death of the employee, divorce, or legal separation — the employee or their dependent’s health coverage extends to 36 months (which is also the longest period of health coverage).
Yet, the COBRA law only applies to businesses with 20 or more employees.
Therefore, under State continuation of coverage, employers with less than 20 workers must provide employees or their dependents with up to 12 months of health coverage.
Workplace safety in New Jersey
In New Jersey, both federal and state laws regarding workplace safety apply.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) is a federal law that covers private-sector employees and some federal government workers. OSHA’s mission is focused on assuring safe and healthful conditions for workers in the workplace.
OSHA sets safety standards that employers must comply with but also provides training and education about recognized hazards and safety measures in the workplace.
There are 6 main types of hazards in the workplace recognized by OSHA:
- Biological hazards — Mold, pests, insects, etc.
- Chemical and dust hazards — Pesticides, asbestos, etc.
- Work organization hazards — Things that cause stress.
- Safety hazards — Slips, trips, falls, etc.
- Physical hazards — Noise, radiation, temperature extremes, etc.
- Ergonomic hazards — Repetition, lifting, awkward postures, etc.
The authorities are obliged to conduct regular inspections to ensure safety standards imposed by OSHA are in full compliance.
OSHA offices in New JerseyIn contrast, public employees in New Jersey are protected by the New Jersey Public Employees Occupational Safety and Health (NJPEOSH) act.
This act also provides guidelines and safety standards to improve working conditions in the workplace.
Under this act, each employee has the right to anonymously notify the employer or NJPEOSH authorities about hazards in the workplace.
Moreover, employees may even request an inspection if they have any concerns about workplace safety.
PEOSH sets and enforces standards regarding:
- Asbestos in construction and general industry
- Hazardous waste
- Indoor air quality
- Lead in construction
- Occupational noise
Miscellaneous New Jersey labor laws
Finally, we’ll cover some of the miscellaneous labor laws concerning New Jersey such as:
- Whistleblower laws
- Recordkeeping laws
New Jersey whistleblower laws
By the New Jersey Conscientious Employee Protection Act (CEPA), no employer is allowed to discharge, penalize, discriminate, or take any disciplinary action against an employee who decides to “blow the whistle”.
This means that CEPA protects any employee who reports any violation of a law to a supervisor or public body.
CEPA protects any employee who:
- Discloses an activity or practice that they believe is in violation of a law, rule, or regulation
- Works as a physician, nurse, or another licensed healthcare professionals who reports improper quality of medical care
- Reports any criminal or fraudulent activity that may damage any shareholder, client, patient, retiree, former employee, or employee
- Refuses to participate in a criminal or fraudulent activity
The whistleblower is required to notify a public body about any of the foregoing activities via written notice.
New Jersey recordkeeping laws
Each employer in New Jersey is accountable for keeping employee records that must contain:
- Employee name, birth date (if the employee is under 18), social security number (only for those who receive gratuity), and address
- Total hours worked each day and each workweek
- Information regarding employee’s earnings (hourly wages, gross and net earnings, tips, deductions)
- Food or lodging expenses for the employee who receives food or lodging supplied by the employer*
The employer is required to keep the wage and hour records for a period of six years at the place of employment or in a central office in New Jersey.
* In addition to the said recordkeeping requirements, each public works contractor — building schools, roads, hospitals, etc. — must keep a record that also includes the employee’s social security number, craft or trade, overtime hours, and fringe benefits paid in cash to the employee.
Conclusion/Disclaimer
We hope this New Jersey labor law guide has been helpful. We advise you to make sure you’ve paid attention to the links we’ve provided, as most of them will lead you to the official government websites and other relevant information.
Please note that this guide was written in Q2 2022, so any changes in the labor laws that were included later than that may not be included in this New Jersey labor laws guide.
We strongly advise you to consult with the appropriate institutions and/or certified representatives before acting on any legal matters.
Clockify is not responsible for any losses or risks incurred, should this guide be used without further guidance from legal or tax advisors.
Need a simple time clock for employees?
Clockify allows you to track time, attendance, and costs with just a few clicks, for FREE.
Your team can track work time via web or mobile app personally, or you can set up a time clock kiosk from which employees can clock in and out.
Later, you can approve timesheets and time off, schedule shifts, run time card reports, and export everything for payroll (PDF, Excel, link, or send to QuickBooks).